Finding the right bike frame is very important for a fun ride. When you bike frame compare, you ensure your choice fits your body size and riding style perfectly. A bike that fits well makes you more comfortable and helps you ride better. Comparing bike frames can help you avoid pain and injuries later on. Knowing the main measurements will help you pick the best frame.
Key Takeaways
Knowing important bike measurements like stack, reach, seat tube angle, and head tube angle helps you find a bike that fits you. It also matches your riding style.
Bike shape affects comfort, handling, and power. The right fit can reduce pain and make your ride better.
Using bike geometry comparison tools and comparing bikes side-by-side helps you pick the best frame for you.
Test rides are very important. They let you feel how different bike shapes change your ride. They also help you find the best fit.
Working with bike fit experts and adjusting things like saddle height and handlebar position can make you more comfortable and improve your performance.
Key Bike Geometry Measurements

Knowing bike geometry measurements is very important for getting the right fit. Each measurement affects how the bike feels and works. Here are the main measurements you should think about:
Stack and Reach
Stack and reach are two key measurements that define the bike’s frame size.
Stack is the height from the bottom bracket to the top of the head tube.
Reach is the distance from the bottom bracket to the head tube.
These measurements change your riding position and comfort. A longer reach can make you feel stretched out. This is good for speed but might hurt if it’s too long. On the other hand, a shorter reach can make you sit more upright. This is comfy but might slow you down.
Finding the right mix of stack and reach is important. A stack that is too low can hurt your back. A reach that is too long can cause neck and shoulder pain. Look for a stack and reach ratio that fits your riding style. For example, a ratio between 1.4 and 1.6 is often best for a relaxed ride.
Seat Tube Angle
The seat tube angle is another important measurement. It shows the angle of the seat tube compared to the ground.
A steeper seat tube angle puts you more forward over the cranks. This helps you pedal better, especially when climbing or sprinting.
An ideal seat tube angle is about 73 degrees. This balances power and knee comfort. Angles steeper than this can push your knees too far forward, causing pain.
Here’s a quick look at common seat tube angles for different bike types:
Bike Type | Typical Seat Tube Angle (degrees) |
|---|---|
Mountain | 71 – 75 |
Road | 73 – 74 |
Gravel | 71 – 75 |
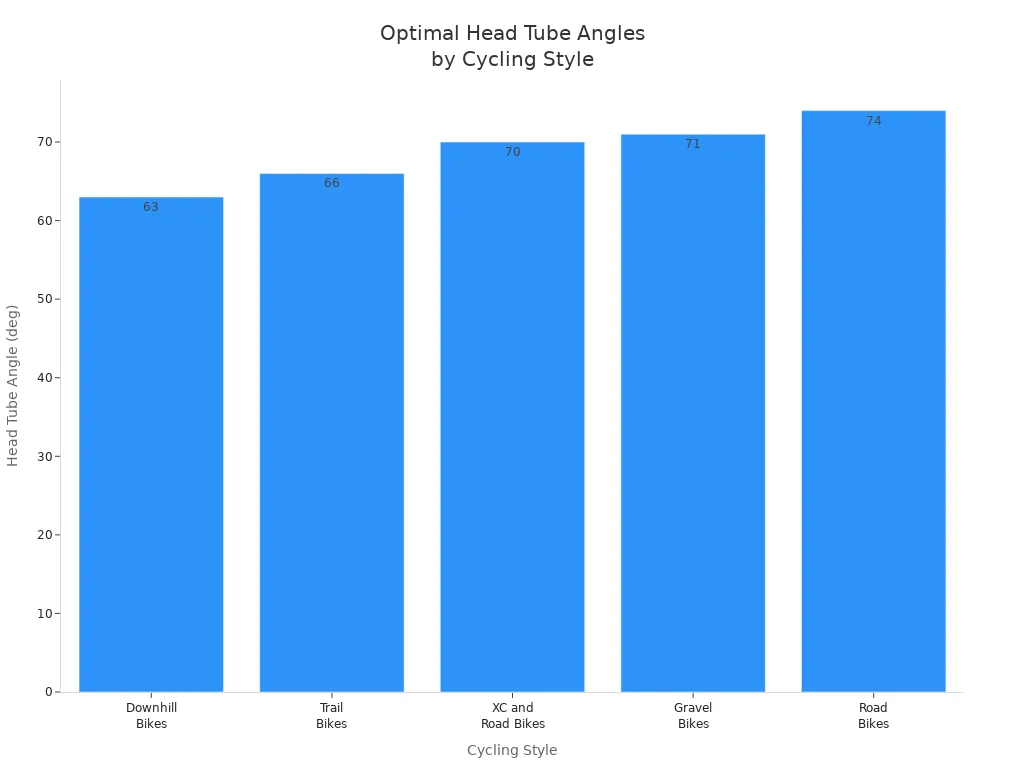
Head Tube Angle
The head tube angle affects how your bike rides.
A steeper head tube angle makes steering quicker and more responsive. This helps with fast turns and tricky riding.
A slacker head tube angle gives more stability. This makes it easier to ride fast without feeling shaky.
Different biking styles need different head tube angles. For example, downhill bikes usually have angles around 62 to 64 degrees for stability. Road bikes often have angles around 74 degrees for quick handling.
Chainstay Length
Chainstay length affects bike handling and rear wheel grip.
Longer chainstays make the bike more stable and help with climbing. They shift weight back, improving rear wheel grip on tough trails.
Shorter chainstays make it easier to turn quickly.
Here’s a summary of how chainstay length changes riding:
Shorter chainstays improve quickness and agility.
Wheelbase
The wheelbase is the distance between the front and back axles.
A longer wheelbase makes the bike more stable, especially at high speeds, but it’s harder to turn.
A shorter wheelbase makes the bike easier to handle in tight spots.
As you compare bike geometries, think about how these measurements work together. The right mix will give you a comfy and efficient ride that fits your style.
Geometry Chart
To see these measurements, check out the geometry chart below:
By knowing these key bike geometry measurements, you can make smart choices when picking a bike frame that fits your needs.
Implications of Bike Geometry on Fit

Bike geometry greatly affects how comfortable you are, how well you handle the bike, and how powerfully you can ride. Knowing these effects helps you pick a bike that fits you and makes your rides better.
Comfort and Riding Position
Your comfort on long rides depends a lot on bike geometry. Important measurements like top tube length and reach decide if you feel stretched out or compact. A taller stack height and shorter reach help you sit more upright. This reduces strain on your neck and back. Endurance bikes usually have these features, making them comfy for long distances.
Research shows that good bike geometry can improve comfort. For example, Richmond (1994) and Matheny (1992) found that handlebar height can affect nerve pressure. This can lead to overuse symptoms. This shows how important it is to choose a bike that matches your body size and riding style.
Handling and Stability
Bike geometry also affects how your bike handles on different terrains. A slacker head tube angle makes the bike more stable. This helps when riding fast. But it can slow down how quickly you steer, which isn’t great for tricky trails. On the other hand, a steeper head tube angle allows for faster steering. This helps when climbing and turning in tight spots.
The link between geometry and handling is very important. For example, a longer wheelbase gives stability, while a shorter one makes it easier to turn. If you want to ride on tough terrain, think about how these measurements work together to create a bike that fits your needs.
Power Transfer
Power transfer is another key part affected by bike geometry. A bike that fits well lets you push energy from your legs to the pedals easily. The seat tube angle is very important here. A steeper angle puts you over the cranks, which helps your pedaling power, especially when climbing.
Studies show that a good bike fit can improve your performance. For instance, cyclists who keep a forward hip position often pedal more effectively. This shows how bike geometry connects to better cycling performance. It’s important to find the right frame fit for your body.
Comparing Bike Geometries
When you look at bike geometries, you can choose the best bike frame for you. There are many tools and methods to help you with this.
Geometry Comparison Tools
Using a bike geometry comparison tool can make finding the right bike frame easier. These tools let you see and compare different bike geometries side by side. Here are some popular choices:
Bike Insights: This tool shows bike-on-bike geometry comparisons with pictures. It also has great search features and helps with sizing.
Velogic Fit: Their free Frame Comparison tool lets you compare two or more bike frames together. You can see frame geometry, images, and details. It even lets you change stem length and angle for the best bike setup.
Geometry Geeks: This site helps you compare many bike geometries in a table format. This makes it easy to spot differences quickly.
These bike geometry comparison tools are popular among cyclists and bike fit experts. They help you see and understand bike frame differences, making your bike choice and fitting easier.
Side-by-Side Comparisons
Making a side-by-side comparison table is a smart way to look at different bike geometries. Here are some important factors to include in your comparison:
Key Factor | Description / Importance | Example / Note |
|---|---|---|
Stack | Vertical distance from the bottom bracket to the handlebar/stem area; influences cockpit height | Important for fit; combined with reach defines hand position relative to legs |
Reach | Horizontal distance from the bottom bracket to the handlebar/stem; affects cockpit reach | Useful for MTB; for road bikes, effective top tube length (TTh) may be more relevant |
Seat Tube Angle (STa) | Angle of the seat tube; affects saddle position relative to the bottom bracket and saddle setback | 1° difference can move saddle setback by ~0.6 inches (11-13mm) |
Effective Top Tube (TTh) | Horizontal length between head tube and seat tube intersection; can be misleading if STa and seatpost setback vary | Should be considered with STa and seatpost setback for accurate fit comparison |
Head Tube Angle (HTa) | Angle of the head tube; influences handling characteristics | Important for handling; experienced riders focus on this and wheelbase |
Chainstay Length | Length of the chainstay; affects handling and stability | Part of handling-related measurements |
Wheelbase | Distance between front and rear wheel axles; affects handling and ride feel | Experienced riders often use this to gauge handling |
By adding these factors to your comparison table, you can better see how different bike geometries will change your riding experience.
Test Ride Considerations
Test rides are very important for checking how geometry numbers feel in real life. Even small changes in bike geometry can really change how it rides. Here’s how different geometry terms affect your ride:
Geometry Term | Effect on Ride Experience | Lower Value Effect | Higher Value Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
Head Tube Angle | Steering & Stability | Slower steering, more stable at speed | Faster steering, less stable, more responsive |
Seat Tube Angle | Pedaling Efficiency & Rider Position | More relaxed, weight further back | More efficient climbing position, weight forward |
Reach | Horizontal Riding Position | Upright, compact cockpit | Stretched, aggressive fit |
Stack | Vertical Riding Position | Lower front, more aerodynamic | Higher front, more comfortable |
Test rides help you check and adjust your expectations based on geometry charts. They make sure the bike fits your body and riding style. Always make test rides a priority to find the best fit for you.
Tips for Optimal Bike Fit
Consult with Experts
When you want the right bike fit, talking to bike fitters is very important. They help you choose the best bike type, model, and size for your body and riding style. Here are some reasons to work with experts:
They help you invest wisely by picking the right bike.
You will feel more comfortable and lower your injury risk with proper joint placement.
Experts make you safer by boosting your confidence and focus while riding.
They improve your performance by adjusting your bike for better power transfer and muscle use.
You get advice on gear and budget, helping you make smart choices.
Special fitting tools allow for exact changes that fit your needs.
Adjustability and Customization
Changing your bike can really boost your comfort and performance. Here’s a table showing common bike fit changes and their effects:
Adjustment | Impact on Rider Comfort and Performance |
|---|---|
Saddle Height | Boosts power by up to 9%; lowers knee stress; too high can strain hamstrings and back; too low can cause knee pain and less efficiency. |
Saddle Fore/Aft | Affects knee position over the pedal; too far forward raises knee pressure; too far back can tighten hamstrings and strain the back. |
Saddle Tilt | Affects pelvic stability and pressure; forward tilt can numb hands/wrists; backward tilt can hurt the back and cause saddle sores. |
Handlebar Reach/Drop | Affects upper body comfort and aerodynamics; too long reach can numb neck, shoulders, and hands; too short can feel cramped and less efficient. |
Cleat Position | Important for knee alignment and pedaling; wrong placement can cause knee pain, foot numbness, and hot spots; small changes can lower strain and boost power transfer. |
These changes help keep your body working well and your muscles active, leading to a better ride.
Personalizing Fit
Making your bike fit just for you is key for comfort and performance. Think about your riding style, body size, and what you like. A personalized fit lets you ride longer without pain. It also helps you keep a better pedal stroke.
Remember, a bike that fits well makes your rides more enjoyable. It helps you have fun while lowering the chance of injury. Spending time on bike fitting is worth it, especially for long rides or competitive cyclists.
Picking the right bike frame is very important for your comfort and how well you ride. Pay attention to key measurements like stack and reach. These help you compare frames from different brands. New studies show that even small changes in geometry can change your ride a lot. For example, a 1-degree change in head tube angle can affect how stable and responsive your steering is.
Always make test rides a priority to see how a bike feels. Knowing these geometry numbers will help you make smart choices. A bike that fits you well makes your rides better, making every trip fun and efficient. 🚴♂️
FAQ
What is the best way to measure my bike frame size?
To find your bike frame size, stand over the bike. Make sure there is 1-2 inches of space between you and the top tube. Use a tape measure to check your inseam length. Then, compare it with the size chart from the manufacturer.
How do I know if a bike fits me properly?
A bike that fits well lets you reach the handlebars easily. Your knees should line up over the pedals. You should feel balanced while riding. Test rides help you see how comfortable and in control you feel.
Can I adjust my bike if it doesn’t fit perfectly?
Yes! You can make many changes. You can change the saddle height, move the saddle forward or back, and adjust the handlebar height. These changes can really help your comfort and performance.
Why is bike geometry important for my fit?
Bike geometry affects how you sit, your comfort, and how the bike handles. Good geometry helps you pedal efficiently and lowers the chance of injury. Knowing these measurements helps you pick the right bike for you.
Should I consult a professional for bike fitting?
Yes, talking to a professional bike fitter can make your ride better. They give you personal adjustments based on your body size and riding style. This can lead to more comfort, better performance, and less chance of injury.
See Also
How To Choose The Perfect Bike Frame For You
Steps To Accurately Measure Your Bike Frame Size
Key Factors To Consider When Comparing Bike Frames