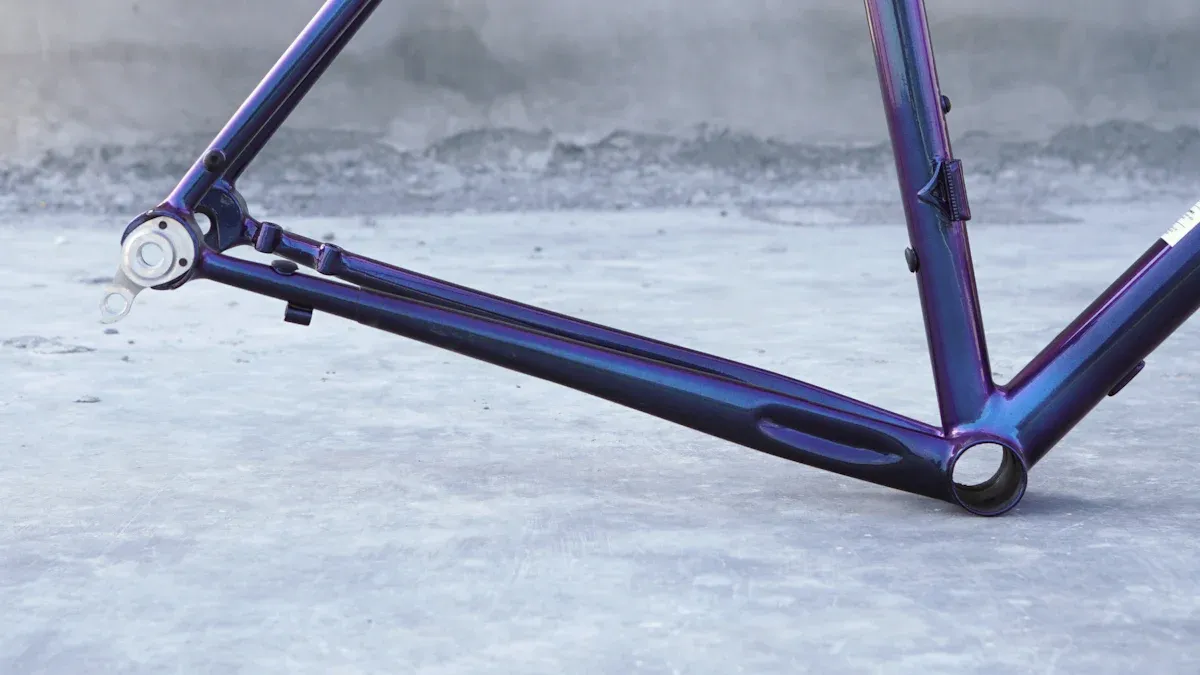
The rear triangle bike frame is very important for your overall cycling experience. It contains key components that significantly affect how your bike operates. A well-designed rear triangle bike frame enhances your ride stability, allowing you to maintain better control while cycling. Additionally, it contributes to your comfort by absorbing bumps and vibrations. Understanding the function of the rear triangle bike frame can assist you in selecting a bike that aligns more closely with your riding style.
Key Takeaways
The rear triangle is important for bike stability and control. A good rear triangle makes your ride better by improving handling.
Chainstay length changes how the bike handles. Longer chainstays give stability, while shorter ones help with quick turns. Pick what fits your riding style.
Flexibility in the rear triangle makes riding more comfortable. A flexible design absorbs bumps and keeps the rear wheel on the ground, which helps grip.
The choice of material is important. Carbon fiber is strong and light, making it great for performance bikes. Think about materials that match your riding needs.
Adjustable rear triangles let you customize your bike. You can change chainstay length and bottom bracket height for different riding styles and terrains.
Rear Triangle Parts

The rear triangle has three main parts: chainstays, seatstays, and rear dropouts. Each part is important for how well your bike works and lasts.
Chainstays
Chainstays connect the bottom bracket to the rear dropouts. Their length affects how your bike handles, speeds up, and climbs. A longer chainstay can make your ride more stable, especially when going downhill. Designers choose chainstay length based on riding style, rider size, and terrain. For example, if you like mountain biking, longer chainstays can help you control your bike better on rough trails.
Seatstays
Seatstays go from the top tube to the rear dropouts. They affect the bike’s weight and strength. Thinner seatstays can lower drag, making your bike lighter and faster. But they must still be strong enough for regular use. Here’s a quick look at how different seatstay designs change weight and strength:
Aspect | Evidence |
|---|---|
Weight | |
Durability | Seatstays can be thin because they are strong under pressure, keeping their shape during use. |
Manufacturers say that dropped seatstays allow for more flex, which makes rides more comfortable. This flex depends more on the shape and materials than the length of the seatstays.
Rear Dropouts
Rear dropouts are where the rear wheel connects to the frame. They come in different designs, which affect wheel alignment and maintenance. For example, horizontal dropouts make it easy to adjust chain tension, so they are popular on fixed-gear bikes. On the other hand, vertical dropouts are common on road bikes, where chain placement is less important. Misaligned dropouts can cause uneven tire wear and tracking problems, which might need professional fixing or replacement.
Knowing these bike frame parts helps you see how they work together to improve your cycling experience.
Functions of the Rear Triangle
The rear triangle is very important for how well your bike works. It helps with strength, power transfer, and flexibility. All these things affect how you ride.
Structural Integrity
The rear triangle gives support to the bike frame. It connects the back wheel to the main frame. This connection keeps the bike stable while you ride. A good rear triangle can handle the forces when you pedal and steer.
Key Points:
A strong rear triangle stops frame flex, which can cause loss of control.
It helps keep the bike’s shape, making it handle well.
When you pedal, the rear triangle needs to resist bending and twisting. This resistance is important for keeping your bike aligned and working well. If the rear triangle is weak, you might have problems like bad handling or even a broken frame.
Power Transfer
Power transfer is about how well your pedaling energy moves through the bike frame to the wheels. The rear triangle plays a big part in this.
Frame Design: Different designs change how power goes from your legs to the road. For example, a diamond frame has been used for over a hundred years. It has both front and rear triangles. Shorter chainstays in this design can help you speed up faster but might cause flexibility problems that affect power transfer.
Here’s a quick look at how different frame designs affect power transfer:
Frame Design | Key Features | Impact on Power Transfer |
|---|---|---|
Diamond Frame | Standard design for over a century | Shorter chainstays can speed up faster but may cause flexibility issues affecting power transfer. |
Stiff Frame | Gives a direct ride feel and better power transfer | Too much stiffness can hurt cornering grip and braking. |
You want a good mix of stiffness and flexibility. More stiffness usually means better power transfer, but too much can make your ride feel rough over bumps.
Flexibility and Compliance
Flexibility in the rear triangle helps your bike follow the ground and soak up shocks. This flexibility lets the back wheel move over obstacles, improving grip and comfort.
Impact on Wheel Tracking:
A rear triangle that is too stiff can make the wheel lose contact with the ground, causing bad handling.
Flexibility helps the rear wheel stay on the ground, which is very important on bumpy surfaces.
Here’s how flexibility affects your ride:
Aspect | Impact on Wheel Tracking and Ride Comfort |
|---|---|
Stiffness of Rear Triangle | |
Compliance Directions | Roll: Helps the rear wheel move over obstacles; Wag: Stops the wheel from being knocked off track, but too much can cause steering problems. |
The flexibility in the rear triangle also helps with vibration damping. It absorbs road vibrations, making your ride more comfortable and reducing tiredness on long rides. However, how well this works depends on the frame design, materials, rider weight, and riding style. Stiffer frames might pass on more shock, while flexible frames give a smoother ride.
Impact on Handling and Stability
The rear triangle is very important for how your bike handles and feels on the road. Its design affects your control, comfort, and overall riding experience. Knowing these details can help you pick a bike that fits your needs.
Handling Characteristics
The shape of the rear triangle greatly changes how your bike handles. Important factors are the length of the chainstay and the height of the bottom bracket (BB).
Longer Chainstays: These make a longer wheelbase, which improves stability. You will see better tracking in a straight line, especially at high speeds or on bumpy surfaces.
Shorter Chainstays: These allow for quicker handling. You can turn tight corners and navigate tricky sections easily. But this might reduce some stability.
Changing the rear triangle shape can move your center of gravity (CoG) back. This change affects how your bike turns. A lower BB height can also improve stability by lowering your CoG without changing the wheelbase.
Here’s a quick overview of how these factors affect your ride:
Parameter | Impact on Riding | Notes |
|---|---|---|
Affects control sensitivity and stability | Longer chainstays improve stability but may slow down agility; shorter ones boost responsiveness. | |
BB Drop/BB Height | Influences riding stability | A larger drop lowers the center of gravity, improving stability but risks bottoming out. |
Seat Tube Angle | Affects riding posture and leg power | Steeper angles help with pedaling efficiency and aerodynamics; common angles are 73-74 degrees. |
Comfort and Ride Quality
The way the rear triangle is built affects your comfort and ride quality on different surfaces. A good mix of stiffness and flexibility is key for the best performance.
Stiff Rear Triangle: While it can give direct power transfer, it may cause wheel misalignment. This misalignment can lead to discomfort and less grip on uneven ground.
Flexible Rear Triangle: Some flex helps the rear wheel stay in contact with the ground. This flexibility absorbs shocks and vibrations, making your ride smoother.
User surveys show that balancing roll and wag in the rear triangle is important for predictability and handling, especially on rough terrain. Here are some key points to remember:
A stiff rear triangle can cause wheel misalignment, while some flex helps the wheel stay on the ground better.
The balance between roll and wag affects predictability and handling, especially on rough terrain.
Innovations in Rear Triangle Design

Bike frame technology has improved a lot, especially in the rear triangle. New materials and shape changes help make bikes perform better and feel more comfortable.
Material Choices
Today’s bike frames often use new materials to be stronger and lighter. Carbon fiber is the strongest choice. It has strengths between 3,500 to 6,000 MPa, which is much better than metals like aluminum and steel. This strength helps create a light design, perfect for racing. Here’s a quick look at common materials used in rear triangles:
Material | Strength (MPa) | Weight (relative) | Corrosion Resistance | Stiffness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Aluminum Alloys | 400 – 700 | Moderate | Good | Moderate |
Titanium Alloys | 900 – 1,200 | Moderate | Excellent | Low |
Magnesium Alloys | Higher than Aluminum | Light | Poor (improved with alloys) | Low |
Carbon Fiber | 3,500 – 6,000 | Very Light | Excellent | High |
Manufacturers are also trying hybrid designs that mix carbon fiber and aluminum. This method improves performance while keeping costs down. For example, carbon-reinforced aluminum frames are strong in tough spots but still light.
Geometry Adjustments
Adjustable rear triangle designs let you change your bike for different riding styles. You can change the chainstay length and bottom bracket height to fit your needs. Here are some important features:
Adjustable Rear-End Length: Change for racing, touring, or mountain biking.
Bottom Bracket Height: Adjust for different terrains.
Flip Chips: Switch between wheel sizes (29″ or mullet) for better performance.
Removable Seat Stay Brace: Adjust stiffness for traction or support.
These new ideas help you get the best ride possible, whether you want speed, comfort, or handling. A well-made rear triangle can fit your riding style and body shape, making your experience enjoyable on any terrain.
In short, the rear triangle bike frame is very important for your cycling experience. It helps with power transfer, handling, and stability. A good rear triangle adds strength and stiffness, which is key for moving energy efficiently. Many modern bikes have a diamond-shaped frame with two triangles, making them strong and light.
Experts say that a strong rear triangle keeps your pedaling efficient, so you don’t waste energy. This design is crucial for racing bikes. When you think about your next bike, keep in mind that the shape and materials of the rear triangle can greatly affect your comfort and ride quality.
FAQ
What are dropouts in a bike frame?
Dropouts are the slots where the back wheel connects to the bike frame. They help keep the wheel straight and make it easy to take the wheel on and off. If the dropouts are aligned correctly, your ride will be smooth and your tires won’t wear unevenly.
How does frame geometry affect bike performance?
Frame geometry changes how a bike rides and feels. It affects how stable, responsive, and comfortable the bike is. A good design can make your ride better and help you control the bike on different surfaces.
Can I adjust the rear triangle for different riding styles?
Yes, many new bikes let you change the rear triangle. You can adjust the chainstay length and bottom bracket height to fit your riding style, whether you are racing, touring, or mountain biking.
How do I know if my dropouts are misaligned?
If you see uneven tire wear or have trouble shifting gears, your dropouts might be misaligned. Check the wheel alignment and look for gaps between the wheel and frame. If you need help, ask a bike mechanic to make adjustments.
What materials are best for rear triangles?
Common materials for rear triangles are aluminum, titanium, and carbon fiber. Each material has different strengths, weights, and stiffness. Choose based on your riding style and what you prefer for performance and comfort.
See Also
Understanding How Mountain Bike Frames Achieve Compliance
Key Differences Between Triathlon And Time Trial Bike Frames
A Guide to Bike Frame Components and Their Roles
Simplifying Large Sizing and Geometry for Mountain Bike Frames
The Importance of Bike Frame Angles for Comfort and Handling