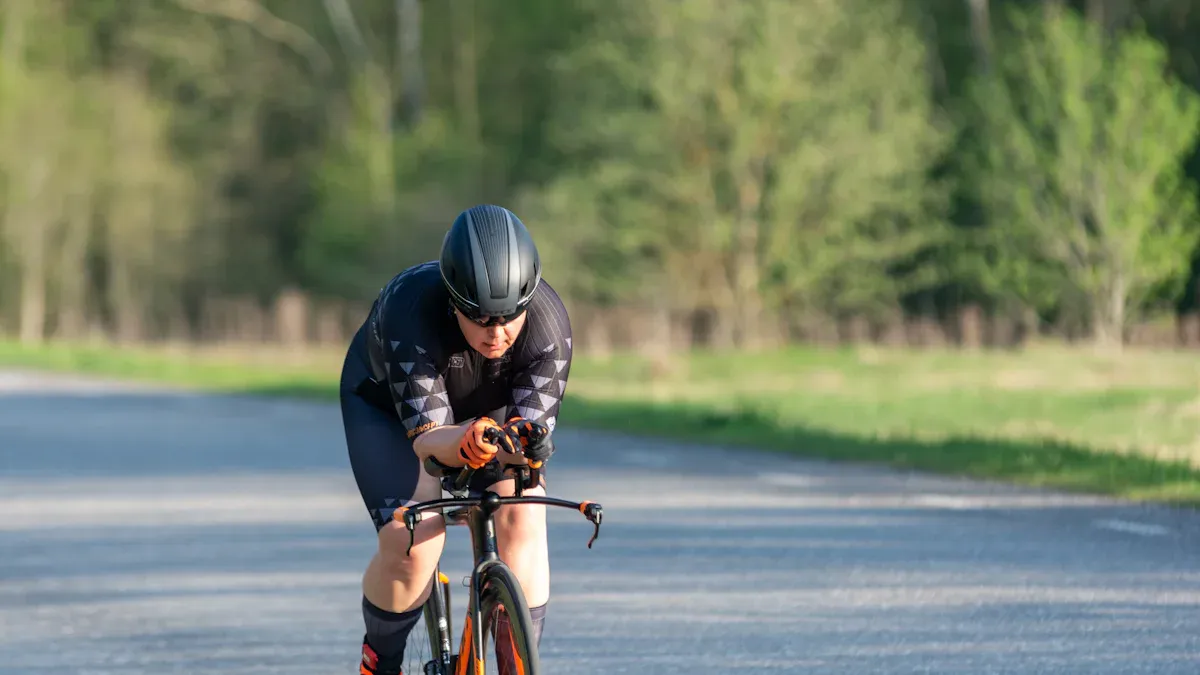
When you ride a road bike, the road bike frame design significantly impacts your performance. Aerodynamics plays a crucial role in determining your speed and energy efficiency. Did you know that the bike frame contributes to 4-9% of a cyclist’s total drag? This highlights that enhancing road bike frame design can help you ride faster and conserve energy. How does the shape of your frame influence your ride? What materials can enhance your aerodynamics? Understanding these factors can greatly improve your cycling experience.
Key Takeaways
Aerodynamics is very important for cyclists. It affects how fast they go and how much energy they use. A good bike frame can lower drag by 4-9%.
The shape of the bike frame changes your riding position. A proper fit helps you ride better and feel more comfortable.
Different materials like carbon fiber, aluminum, and steel change weight and strength. Carbon fiber is light and strong, which is great for speed.
Frame geometry, like tube angles and lengths, affects stability and aerodynamics. Steeper angles can help reduce wind resistance.
Finding the right mix of comfort and performance is important. Try different bikes to find what works best for your riding style.
Anatomy of a Bicycle Frame
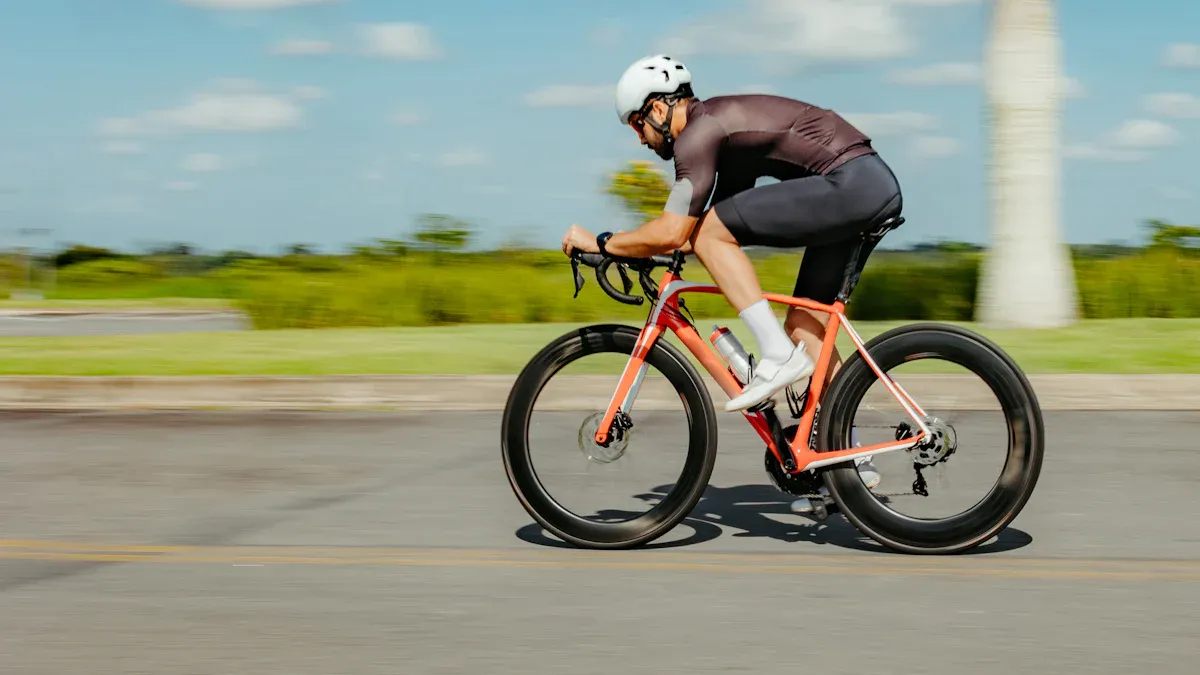

Knowing the parts of a bicycle frame is important for every cyclist. The frame is like the backbone of your bike. It affects how well you perform and how comfortable you feel. Let’s look at the main parts and see how frame shape helps with aerodynamics.
Key Components
A bicycle frame has several important parts that work together. These parts help create a smooth and stable ride. Here are the main parts you should know:
Top Tube: This tube goes across from the seat tube to the head tube. It affects how far you reach and how the bike fits you.
Down Tube: This tube runs from the head tube down to the bottom bracket. It gives strength and stability.
Seat Tube: This vertical tube holds the saddle and changes your riding position.
Chainstays: These tubes connect the bottom bracket to the rear axle. They affect how quickly the bike responds and how power is transferred.
Seatstays: These tubes link the top tube to the rear axle. They help absorb bumps and make your ride more comfortable.
Each part helps the bike perform better. For example, a shorter top tube can make you lean forward more, which can help with aerodynamics.
Frame Geometry
Frame geometry means the angles and lengths of the tubes in the frame. Knowing these details is key for better aerodynamics and handling. Here are some important parts of frame geometry:
Head Tube Angle: A steeper head tube angle (like 73°) helps with quick steering and a more aggressive position. This reduces the area facing the wind, improving aerodynamics. A slacker angle (like 65°) makes the bike more stable but can increase drag.
Seat Tube Angle: This angle affects how efficiently you pedal and your comfort. Sitting more upright can feel better but might hurt aerodynamics.
Top Tube Length: A longer top tube stretches your body out, which can lower wind resistance. But it might also make long rides less comfortable.
Chainstay Length: Longer chainstays can make the bike more stable, especially when going fast. However, they might make the bike feel less quick.
The shape of your bike greatly affects how it handles, how comfortable it is, and its aerodynamics. A good design helps you stay in a strong position without losing comfort. Modern aerodynamic bikes usually have a shorter head tube and a longer reach, which helps cut down wind resistance.
In racing, frame geometry has changed to focus on speed. Aerodynamic bikes often have a thinner, flatter shape, which helps them move through the wind better. Built-in parts also reduce wind resistance, making these bikes great for racing.
By knowing these important geometry details, you can choose a bike that fits your riding style and goals.
Geometry and Aerodynamics

It is important to know how geometry affects aerodynamics for better road biking. The angles and lengths of the tubes in your bike frame are very important for how well you perform. Let’s look at how these things change your ride.
Tube Angles
The angles of the tubes, especially the head tube and seat tube angles, affect your riding position and wind resistance. A bike with aggressive geometry has steeper angles. This design lowers your body, which makes you face less wind. As a result, you feel less wind resistance, which helps your performance.
On the other hand, a relaxed geometry puts you in a higher, more upright position. This is more comfortable for long rides but increases wind resistance. Here’s a quick comparison:
Bike Type | Geometry Type | Rider Position Description | Wind Resistance Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
Competition Road | Aggressive | Lower and more forward, with a flatter back and pronounced forward lean | Reduced |
Endurance Road | Relaxed | More upright, providing stability and comfort for long-distance riding | Increased |
Wind tunnel tests show that changing tube angles can greatly reduce drag. Testing at different yaw angles helps us see how these changes affect performance. However, simple models may not show all the details of real-world riding.
Lengths and Stability
The lengths of the tubes are also very important for your bike’s stability and aerodynamics. For example, a longer wheelbase makes the bike more stable, especially when going fast. This design helps you stay in control during fast descents or sharp turns. However, it might make your bike feel less quick.
The top tube length also affects your riding position. If the top tube is too long or too short, it can change your comfort and control. Here’s a summary of how these parts work together:
Component | Effect on Stability | Effect on Aerodynamics |
|---|---|---|
Wheelbase | Longer wheelbase increases stability, especially at high speeds. | Affects handling but less directly related to aerodynamics. |
Top Tube Length | Affects rider’s position; too long or too short can impact comfort and control. | Affects aerodynamics by influencing rider’s posture. |
Also, a slacker head tube angle can make the bike more stable by stretching the front-to-center distance. This design helps you ride straight, especially at high speeds. On the other hand, shorter chainstays help aerodynamics by covering the rear wheel, balancing weight for better handling.
Materials in Road Bike Frame Design
When you pick a bike frame, the material is very important for how well you ride. Each material has special features that change weight, strength, and how smooth your ride feels. Let’s look at the most common materials: aluminum, carbon fiber, and steel.
Aluminum vs. Carbon Fiber
Aluminum frames are popular because they are light and cheap. They perform well but can be heavier than carbon fiber. Carbon fiber frames are known for being very strong and light. You can have a lighter bike without losing strength. This is great for road biking since lighter bikes help you go faster and use less energy. Here are some important points to think about:
Carbon’s strong stiffness-to-weight ratio helps power transfer from pedaling.
This efficiency is key for going fast in road biking.
Material | Weight Difference | Impact on Speed and Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
Carbon Fiber | Up to 1 pound | Better acceleration and handling because it is lighter. |
Aluminum | Heavier | Good performance, but less efficient power transfer. |
Steel Frames
Steel frames have been used in cycling for a long time. They are strong and comfortable, which many cyclists like. But they also have some downsides. Steel frames are usually heavier than aluminum and carbon fiber, which can slow you down in races. The extra weight means you need to be fitter to keep up during competitions.
Material | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
Steel | Durability, Comfort, Repairability | Weight, Rust, Lower Stiffness |
Carbon | Lightweight, Stiffness, Aerodynamics | Less comfortable on long rides |
While steel frames can last for many years with care, they might not be the best choice for serious racing. The extra weight makes them less ideal when every ounce matters.
Balancing Comfort and Performance
Importance of Fit
Getting the right bike fit is very important for a good ride. A bike that fits you well helps reduce wind drag. This means you can go faster with less effort. Studies show that if you lower drag by 10%, you can save over 1 minute and 30 seconds in a 40km race. However, if you lower your torso angle, you might lose up to 15% of your power. Still, the benefits of better aerodynamics usually outweigh this power loss.
A good bike fit not only helps you ride better but also helps prevent injuries. Research shows that fitting your bike properly can lower pain, discomfort, and tiredness over time. This is important for keeping you cycling for a long time and improving your performance. When your bike fits you well, you can ride longer and feel more comfortable.
Aerodynamics vs. Comfort
Finding the right mix of aerodynamics and comfort can be hard. Bikes made for speed often have shapes that can be uncomfortable on long rides. These designs help with aerodynamics but may not work for everyone. Many casual cyclists might not have the flexibility or strength for these positions, which can cause pain and tiredness.
On the flip side, bikes made for comfort usually have a more relaxed shape. This design lets you sit up straight, which reduces strain on your body. But this comfort might slow you down. Knowing this trade-off is important when picking the right bike for your style.
In the end, think about what you like and your riding goals. Trying out different bikes and making changes can help you find the best fit. Remember, there isn’t just one perfect frame; the best choice depends on how you plan to use it and what you value more: comfort or performance.
In conclusion, the design of your bike frame is very important for your road biking. Important things like shape, materials, and fit can change how well you ride. Keep these points in mind when picking your bike:
Aerodynamics is one of the most important things for cyclists. It affects how fast you go and how much energy you use.
The shape of the frame changes how you sit and feel while riding. This can help or hurt your performance.
The material you choose affects how heavy and strong the bike is. Options like carbon fiber, aluminum, and steel meet different needs.
When you pick your bike, think about how these parts affect your ride. A good frame design can make your cycling better, helping you ride faster and feel more comfortable. 🚴♂️
FAQ
What does road bike frame design do for speed?
The design of a road bike frame affects how fast you can go. A good frame helps cut down wind resistance. This means you can ride faster and use less energy.
How does the material of the frame change performance?
Different frame materials like aluminum, carbon fiber, and steel have special features. Carbon fiber is light and strong, which helps you go faster. Steel is tough and comfy but usually heavier.
Why is having the right fit important in road biking?
A good fit makes riding more comfortable and helps reduce drag. When your bike fits you well, you can stay in a good position without losing power or getting hurt.
Can I make my bike more aerodynamic without changing the frame?
Yes, you can improve aerodynamics by changing how you sit on the bike, using special handlebars, or wearing tight clothes. These changes can help lower drag without needing to change the frame.
What are the benefits of steel frames for road biking?
Steel frames are strong and comfortable, which is great for long rides. They soak up bumps from the road well, but they are usually heavier than aluminum or carbon fiber frames.
See Also
Factors That Enhance Comfort and Speed in Road Bike Frames
Selecting the Perfect Aluminum Road Bike Frame for You
The Importance of Frame Size for Road Bike Comfort