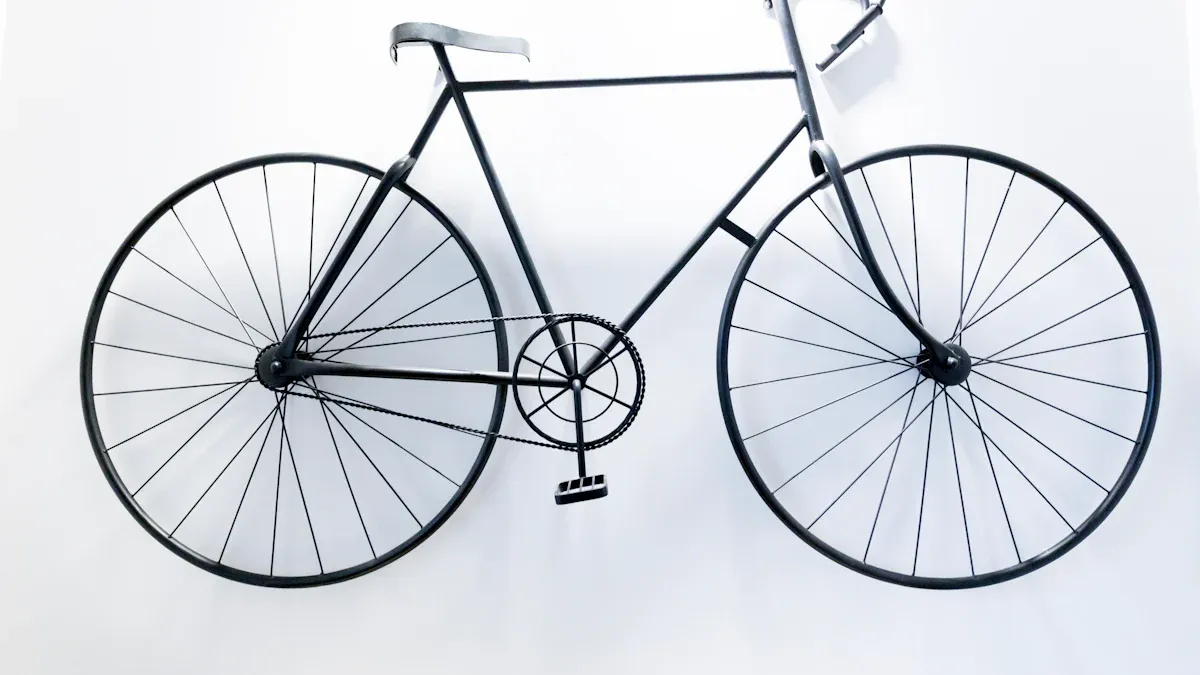
Understanding the anatomy of a bike frame is important for all cyclists. When you know the key parts of the bike frame, you can make smart choices that improve your ride. Here are some benefits of knowing the anatomy of a bike frame:
You can pick a bike that matches your needs.
Understanding the anatomy helps you choose how the bike handles and its weight.
Knowing bike parts helps you talk to shopkeepers. This way, you can make good purchases.
This basic knowledge leads to a more comfortable and fun ride.
Key Takeaways
Knowing bike frame parts helps you pick a bike that works for you and makes your ride better.
The top tube length is important for comfort and how well you ride. A good fit helps your riding position.
The down tube’s size and shape change bike stability and power. A stronger down tube gives you better control while riding.
Picking the right seat tube length and angle is important for comfort. A good fit makes long rides less uncomfortable.
Checking your bike’s parts often keeps you safe and helps it work better. Taking care of your bike prevents injuries and makes cycling more enjoyable.
Top Tube in Bike Anatomy
Overview
The top tube is an important part of your bike frame. It connects the head tube in front to the seat tube in back. This horizontal tube helps hold the bike together. The effective top tube length is a key measurement. It helps you understand bike shape, even if the top tube is slanted.
The effective top tube length helps you know your reach on the bike.
A longer top tube can make you feel stretched out, while a shorter one may feel tight.
Role in Performance
The top tube affects your comfort and how well you ride. A good top tube design helps you keep a proper riding position. This position is important for getting power and comfort during long rides. Studies show that the angle of the seat tube greatly affects cycling performance, like efficiency and muscle use. A steeper angle can improve efficiency by helping you use power better and lowering energy costs.
When you pick a bike, think about how the top tube length affects your fit. A good fit can really improve your comfort, especially on long rides. While some cyclists look at standover height, the top tube length is more important for a good riding position.
Effective Top Tube (ETT) measures the distance from the head tube to the seat tube. This tells you how the bike feels when sitting.
Reach measures the distance from the head tube to a line through the bottom bracket. This tells you how the bike feels when standing.
Both measurements are important for understanding bike fit. A good fit leads to better control and comfort, so you can enjoy your ride more.
Down Tube: Key Component of Anatomy Bike Frame

Overview
The down tube is an important part of your bike frame. It goes from the head tube to the bottom bracket. This tube connects the front and back parts of the bike. Its shape affects how stable and strong the bike is.
When you pick a bike, think about the down tube’s size and shape. A bigger down tube makes the bike stiffer. This stiffness helps with power and control when riding hard. Thicker walls make the frame stronger. The size and thickness let you change your ride to fit your needs.
Importance for Strength
The down tube affects how the bike handles and stays stable. A strong down tube keeps the bike steady while you ride. When you pedal hard, the down tube sends your power to the back wheel. This is important for speeding up and climbing hills.
Here are some key points about the down tube’s strength:
Material Choices: Different materials have different strengths. Common materials include:
Aluminum: Light and stiff, but can wear out faster than others.
Chromoly: Strong and durable, often used in high-end bikes.
Carbon Fiber: Very strong for its weight, great for racing.
Material | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
Steel | Strong, lasts long, responsive, good flex | Heavier than other materials |
Chromoly | Light, strong, durable, keeps its shape | Costs more than regular steel |
Aluminum | Light, strong, stiff, commonly used | Wears out faster than others |
Carbon Fiber | Very light, great strength-to-weight ratio | Can be pricey and less durable |
Titanium | Strong, light, resists rust | Very expensive |
Stiffness and Handling: High stiffness helps with control and handling. This stiffness allows quick reactions to turns, which is important for tricky paths or sharp turns. A stiff frame gives a direct ride, making it feel sharp when speeding up. But, it might also pass on more bumps from the road, which can affect comfort.
Knowing how the down tube works in your bike frame helps you make smart choices. A good down tube design leads to better stability and handling, improving your cycling experience.
Seat Tube: Understanding the Anatomy of a Bike

Overview
The seat tube is an important part of your bike frame. It goes straight up from the bottom bracket to the seat. This tube helps you sit comfortably on the bike. A good seat tube design helps you keep a nice riding position.
Impact on Comfort
The length and angle of the seat tube really affect your comfort while riding. A longer seat tube helps taller riders change their seat height easily. For shorter riders, a smaller frame with a shorter seat tube makes it easier to get on and off the bike.
When picking a bike, think about your inseam and body shape. Choosing the right frame size is very important for comfort. Here are some key points to remember:
Shorter riders may need to pick frame sizes based on height.
Taller riders can change the seat height easier than reaching the handlebars.
A bike that fits well helps reduce discomfort and tiredness on long rides.
The angle of the seat tube also changes how you sit. Most road bikes have a seat tube angle of about 73 degrees. Mountain bikes usually have steeper angles, from 74 to 79 degrees. This change helps with power and control when climbing.
A steeper angle moves you forward, which helps you pedal better. This position is good for people with strong hamstrings and helps with speed on flat roads. On the other hand, a shallower angle moves you back, which helps your quadriceps and glutes, making it easier to climb.
Chainstays: Essential Parts of a Road Bike
Overview
Chainstays are important parts of your bike frame. They connect the bottom bracket to the rear dropouts, where the back wheel attaches. The length and stiffness of chainstays greatly affect how your bike performs and handles.
Connection to Rear Wheel
Chainstays help transfer power from your pedals to the back wheel. When you pedal, the force goes through the chainstays, pushing the bike forward. Here’s how the length of chainstays changes your ride:
Move the center of mass back.
Make it easier to handle and lift the front wheel.
Improve responsiveness, especially during fast sprints.
Move the center of mass forward.
Offer more stability because of extra weight on the front wheel.
Help with seated climbing, making it easier for slow pedaling.
The table below shows how different frame designs affect power transfer:
Frame Design | Key Features | Impact on Power Transfer |
|---|---|---|
Diamond Frame | Standard design for over a century | Shorter chainstays can speed up faster but may cause flexibility issues affecting power transfer. |
Stiff Frame | Gives a direct ride feel and better power transfer | Too much stiffness can hurt cornering grip and braking. |
Stiffer chainstays improve stability when climbing and sprinting. They reduce flex in the rear triangle, which helps keep the wheels on the ground. Less flex means less power loss at the wheel, making acceleration better.
Fork: Backbone of Bike Anatomy
Overview
The fork is an important part of your bike frame. It connects the front wheel to the bike. The fork helps with steering and control. When you turn the handlebars, the fork moves. This lets you steer smoothly. A good fork design helps you steer better. This is very important for safe riding.
Types of Forks
There are different types of forks. Each type changes your ride in different ways:
Rigid Forks: These forks have no suspension. They give a direct feel to the road. This improves power transfer. But, they also send every bump to you. This makes rough rides less comfy.
Suspension Forks: These forks soak up bumps and holes. They help reduce tiredness on long rides. They might take away some energy, but they make rides much more comfortable.
Here are some key points about fork designs:
Comfort First: Suspension forks soak up shocks and lower tiredness. Rigid forks send every bump to the rider.
Handling & Feel: Fork stiffness is key for good steering. Soft forks can make steering unclear.
Efficiency Trade-off: Rigid forks are great for power transfer on smooth roads. Suspension forks might lose some energy but boost comfort.
The material of the fork also affects your bike’s performance. Here’s a comparison of common fork materials:
Material | Weight | Durability |
|---|---|---|
Carbon Fiber | Very light, great for racing and high performance | Strong but can crack under heavy hits |
Steel | Heaviest option, but very stable | Very strong and lasts long, easy to fix |
Aluminum | Medium weight, lighter than steel but heavier than carbon | Good strength, but not as tough as steel |
Titanium | Light, like carbon but stronger | Very strong, resists rust and wear |
The fork’s design and build can change your bike’s weight and balance. Lighter materials make for a quicker ride. The fork’s shape is also important for speed and performance, especially when going fast.
Knowing how the fork works and its types helps you choose the right bike. A good fork improves your control and comfort, making every ride more fun.
Knowing about bike parts makes your rides better. Each part, like the top tube and fork, is important for your comfort and how well you ride. When picking a bike or changing it, think about how these parts work together.
Keep these important points in mind:
Choosing the right bike size is key for comfort and performance.
Checking your bike often can help avoid injuries and make your ride better.
New bike designs use better materials and shapes, improving your cycling experience.
By paying attention to these things, you can have longer and more enjoyable rides on your road bike frame.
FAQ
What does the drivetrain do in a bike?
The drivetrain sends your pedaling power to the wheels. It has parts like the chain, gears, and derailleurs. A good drivetrain helps with smooth gear changes and better power transfer.
How does the bike frame material change performance?
Different materials affect weight, stiffness, and comfort. Aluminum is light and stiff. Carbon fiber is strong for its weight. Steel is tough but can be heavier.
Why is fitting a bike important?
A good bike fit makes riding more comfortable and helps you perform better. It helps you keep a good riding position, which lowers tiredness on long rides. Changing the seat height and reach can really improve your ride.
Can I change my bike frame?
Yes, you can change your bike frame. Think about the material, shape, and if it fits with your other parts. Make sure your new frame works well with your drivetrain and other components.
How often should I check my bike’s parts?
Regular checks are important for safety and performance. Look at your drivetrain, brakes, and tires before each ride. A full check every few months can help find problems early.
See Also
Understanding Bike Frame Components And Their Key Functions
Key Bike Frame Parts Every Cyclist Must Be Aware Of
Essential Components Of A Bike Frame And Their Functions